
De-Mineralization Plant
Pure Water for High-Performance Industrial Applications
Working Principle of De‑Mineralization Plants
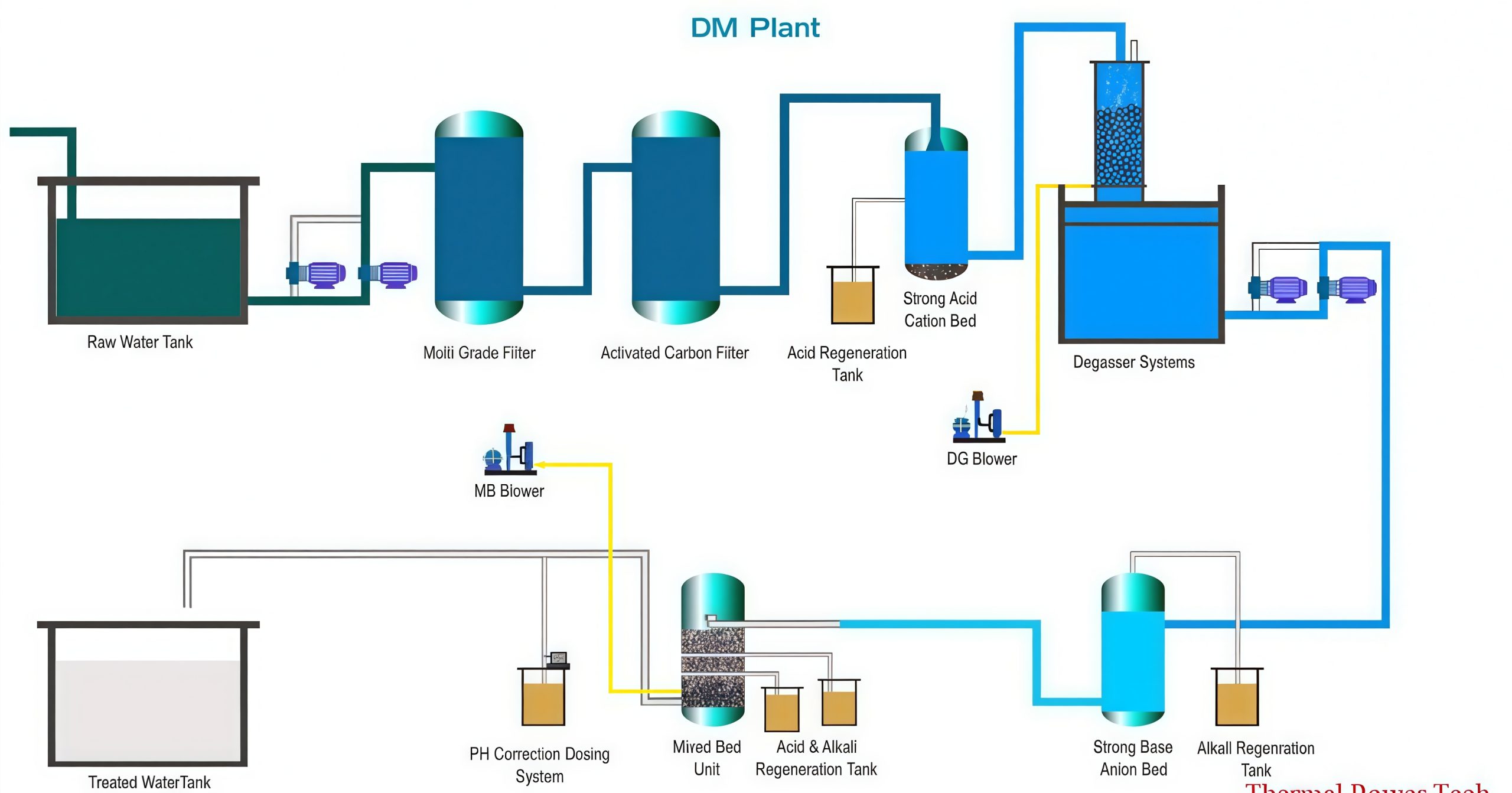
De‑mineralization plants operate on the ion exchange process. Water first passes through a cation exchanger, where positively charged mineral ions are replaced with hydrogen ions. It then flows through an anion exchanger, where negatively charged ions are replaced with hydroxyl ions. The hydrogen (H⁺) and hydroxyl (OH⁻) ions combine to form pure water (H₂O). For higher purity requirements, mixed‑bed resin configurations can be used, where both cation and anion resins are blended to polish the water to extremely low conductivity levels.
Product Variations & Features
- ✔️Capacity: From small lab-scale (liters/hr) to large industrial (m³/hr).
- ✔️Automation: Manual, semi-automatic, fully automatic.
- ✔️Material: FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) tanks are common; SS is also used.
- ✔️Purity: <10 ppm TDS, <2 µS/cm conductivity (can be lower).
- ✔️Design: Compact units, modular systems, containerized plants.
Types of De-Mineralization Plants
Two-Bed DM Plants
Mixed-Bed Units
Package DM Plants
RO DM Plants

Ion Exchange (IX):
Uses cation and anion resins (H⁺ & OH⁻) to exchange unwanted ions from water. Mixed-bed polishing is often used to achieve ultra-pure water quality.

Electrodeionization (EDI):
An advanced polishing process that uses electricity and ion-exchange membranes to produce consistently high-purity water without chemicals.

Reverse Osmosis (RO):
Advanced membrane filtration technology used for effective salt and TDS removal, commonly applied as a pre-treatment stage.

Pre-Treatment System:
Includes pressure sand filters, activated carbon filters, and water softeners to protect membranes and resins, ensuring longer system life.
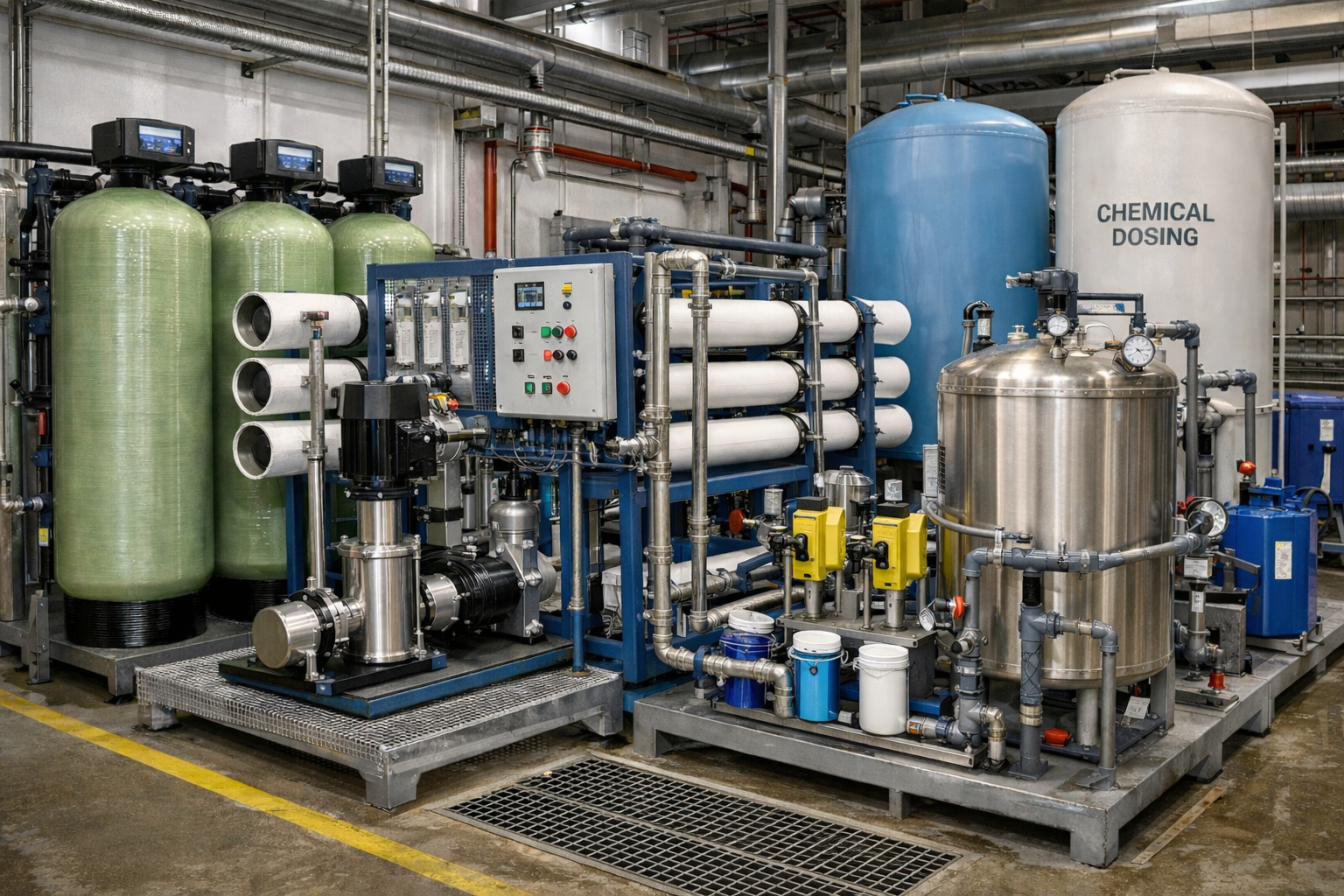
Boiler feed water treatment

Power generation plants

Pharmaceutical and healthcare facilities

Laboratories and research centers

Chemical and process industries
How does a DM Plant work?
Then, it flows through an Anion Exchanger, swapping negative ions (like Chloride, Sulfate) with Hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
The H⁺ and OH⁻ combine to form pure water (H₂O).
Mixed-Bed (MB) System: A single tank with a mix of cation and anion resins offers even higher purity by performing both exchanges simultaneously.
What are its main components?
Cation Resin: Exchanging cations for H⁺.
Anion Resin: Exchanging anions for OH⁻.
Degasser Tower (Optional): Removes carbonic acid formed after the cation exchanger, reducing the load on the anion resin.
Conductivity Meter: Monitors water purity by measuring electrical conductivity (lower conductivity means higher purity).
How is the resin regenerated?
When resins are exhausted, they are regenerated: Cation resin with acid (like HCl) and Anion resin with alkali (like NaOH) to restore their ion-exchange capacity.
Why is DM water better than distilled water?
DM plants can produce high-purity water more economically and at a greater scale than distillation, making it ideal for large industrial needs.
Benefits of using a DM Plant?
- ✔️High-purity water output
- ✔️Prevents scaling and corrosion
- ✔️Improves equipment life
- ✔️Reduces maintenance costs
- ✔️Enhances process efficiency
| Feature | Model A (Compact) | Model B (Medium Scale) | Model C (Industrial) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity (LPH / m³/hr) | 500 LPH | 2000 LPH | 10 m³/hr |
| Automation Grade | Semi-Automatic | Automatic | Fully Automatic (PLC controlled) |
| Feed Water Quality (Max TDS) | 1000 ppm | 500 ppm | Requires Water Analysis |
| Output Water Quality (Conductivity) | < 10 µS/cm | < 1 µS/cm | < 0.5 µS/cm |
| Material of Construction | FRP | FRP / MSRL | MSRL / SS |
| Regeneration Type | Manual | Semi-Auto Chemical | Fully Automatic |
Services & Support
- Installation & Commissioning
- Annual Maintenance Contracts (AMC)
- Spare Parts & Consumables:
Resins, membranes (if RO pre-treatment used), filters, and regeneration chemicals - Water Testing & Consultancy
Ask Your Questions
Our Esteemed Clients

















